Eczema—the word itself can conjure images of dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. But what exactly is eczema, and what triggers these uncomfortable flare-ups? This comprehensive blog article dives deep into the world of eczema, exploring its causes, types, and, most importantly, how to find relief.

What's Eczema?
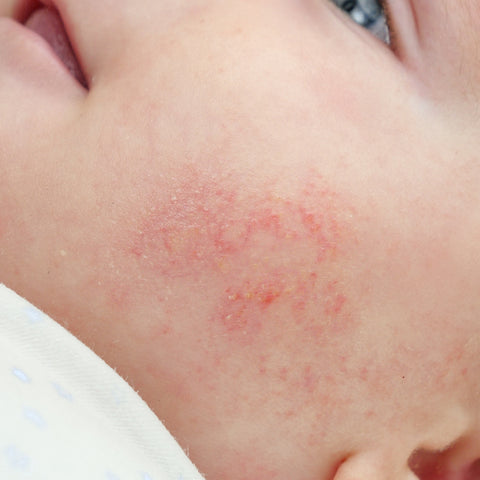
Types of Eczema?
-
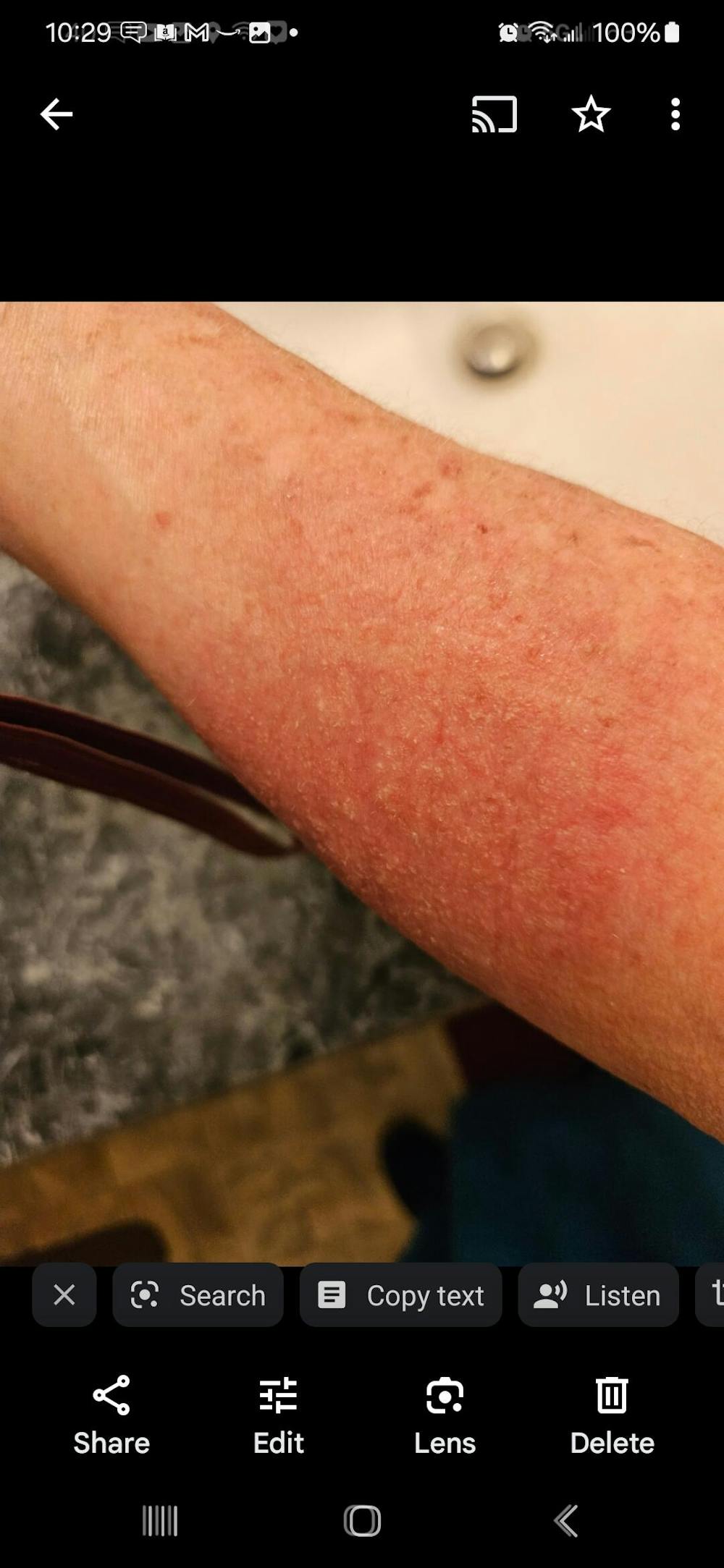
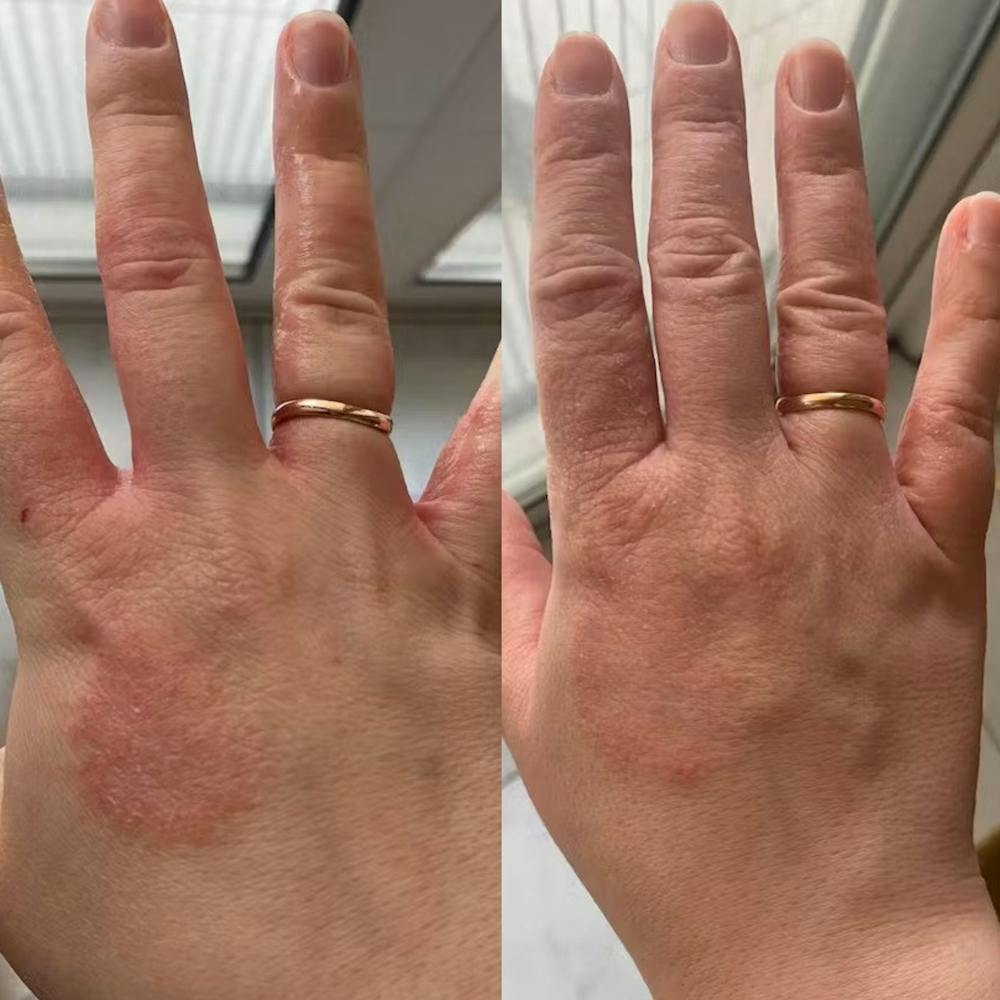
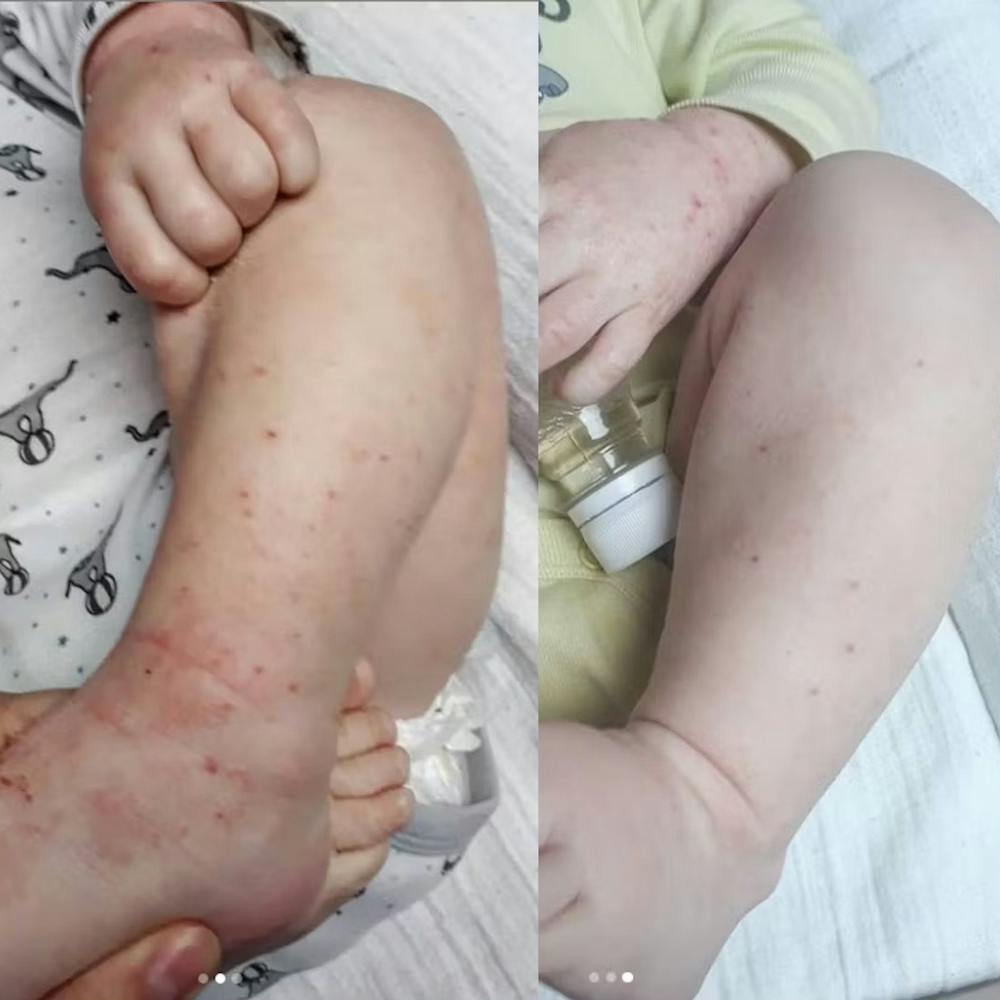
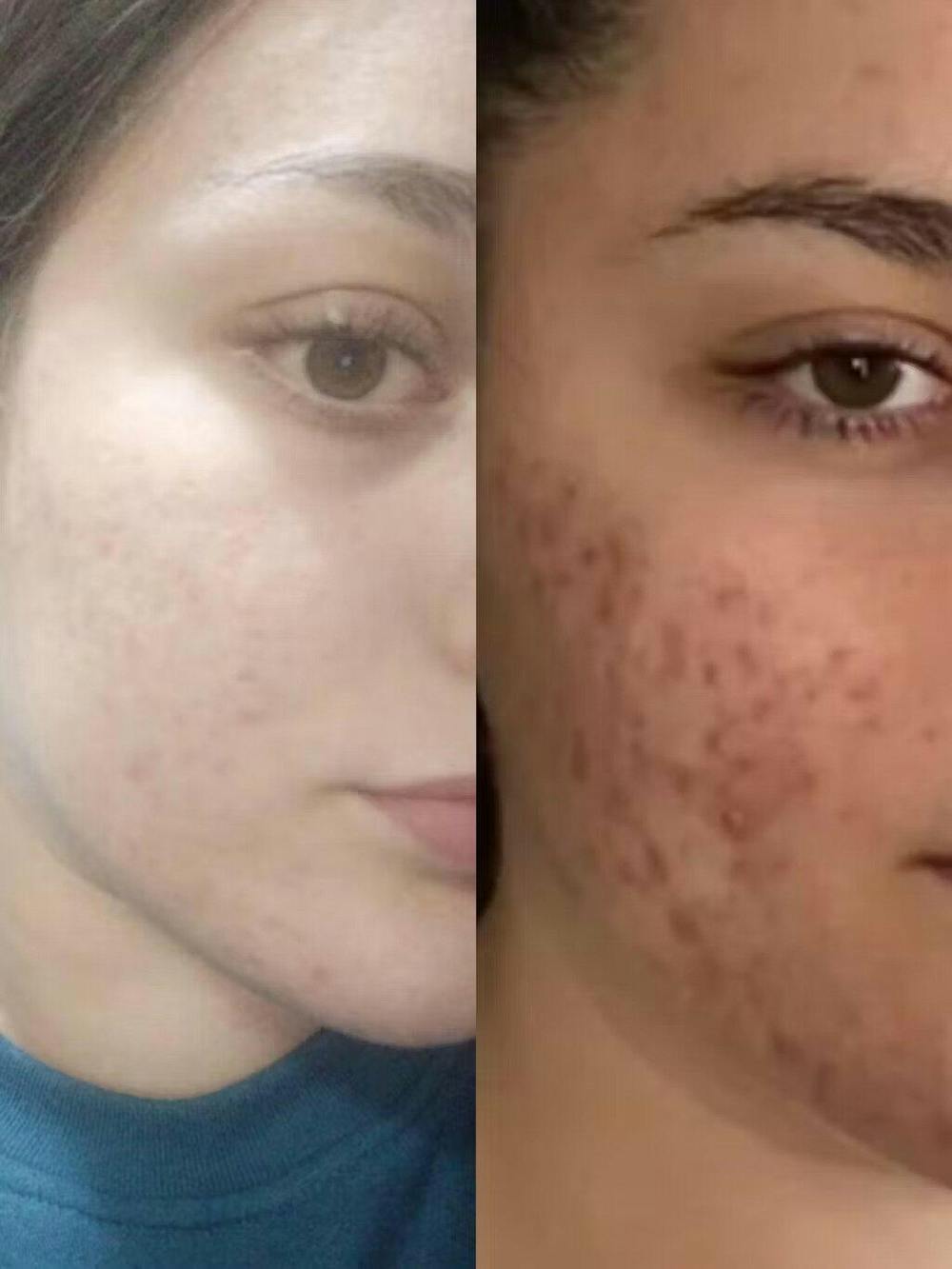
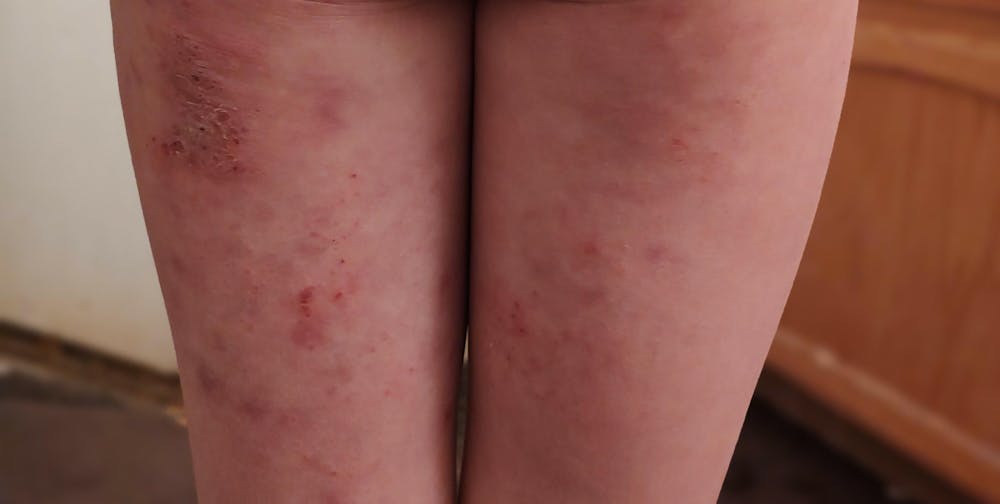
Atopic eczema: The most common type, typically affecting children but can persist into adulthood. It often appears on the face, hands, and inner elbows.
-
Dyshidrotic eczema: It causes small, itchy blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
-
Seborrheic eczema: Characterized by greasy, scaly patches on the scalp, eyebrows, and beard area.
-
Asteatotic eczema: This form is more common in older adults and appears as dry, cracked skin, often on the legs.
Can I Suddenly Develop Eczema?

What Causes Eczema?
- Genetics: Plays a role in skin barrier function and immune system regulation.
- Immune System: Overactivity can lead to inflammation in the skin.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: A compromised barrier allows irritants and allergens to trigger flare-ups.
- Environmental Triggers: Dry weather, dust mites, pollen, irritants, and stress can worsen symptoms.
- Food Allergies: May contribute to eczema, especially in children.
- Harsh chemicals in cosmetics and domestics compromise our skin barrier.
- Stress: While not a direct cause, stress can worsen existing eczema symptoms.
Eczema vs. Dermatitis: What's the Difference?
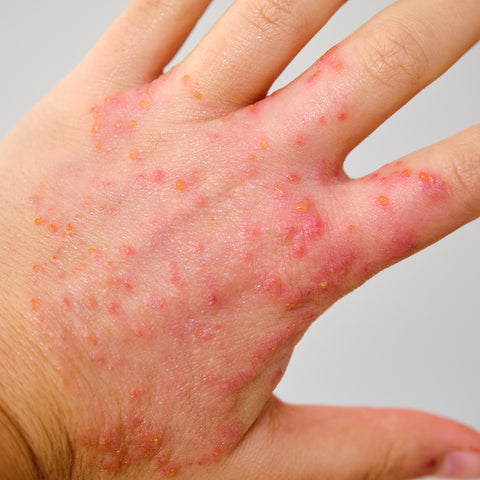
Can Eczema Be Caused by Allergies?
Why is Eczema So Common Now?
-
Increased hygiene: While good hygiene is essential, overly harsh soaps and frequent handwashing can disrupt the skin's natural barrier, making it more susceptible to eczema.
-
Environmental pollution: Exposure to environmental pollutants and chemicals may worsen eczema symptoms.
-
Changes in diet: The rise in processed foods and a decline in gut health might be contributing factors.
-
Many cosmetic and domestic products contain harmful chemicals. Sulphates, parabens, silicones, and many others irritate our skin and have disastrous effects on our bodies.
Since COVID-19 entered our lives, the usage of disinfectants has risen drastically. Disinfectants are a double-edged sword. While they effectively kill germs and bacteria on surfaces and our skin, they can also cause irritation, dryness, allergic reactions and… eczema.
How to Stop Eczema Itching Immediately?
- Moisturize regularly: Using a fragrance-free, gentle moisturizer throughout the day helps maintain the skin's barrier function and reduces dryness.
- Apply a cold compress: A cool, damp cloth on the affected area can provide temporary relief from itching and inflammation.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching may worsen inflammation and increase the risk of infection. Try gently patting the itchy area instead.
- Identify and avoid triggers: If you suspect allergies are a culprit, work with a healthcare professional to identify and avoid your triggers.
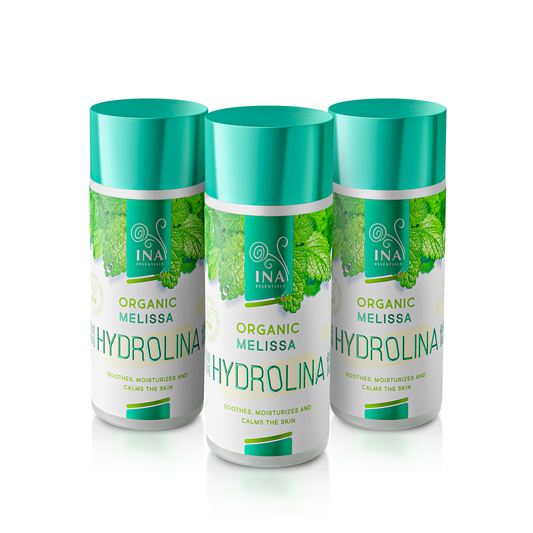
- Use Organic Chamomile water - Hydrolina for Eczema and Irritated skin
Using natural products without any chemical additives can really have an impact.
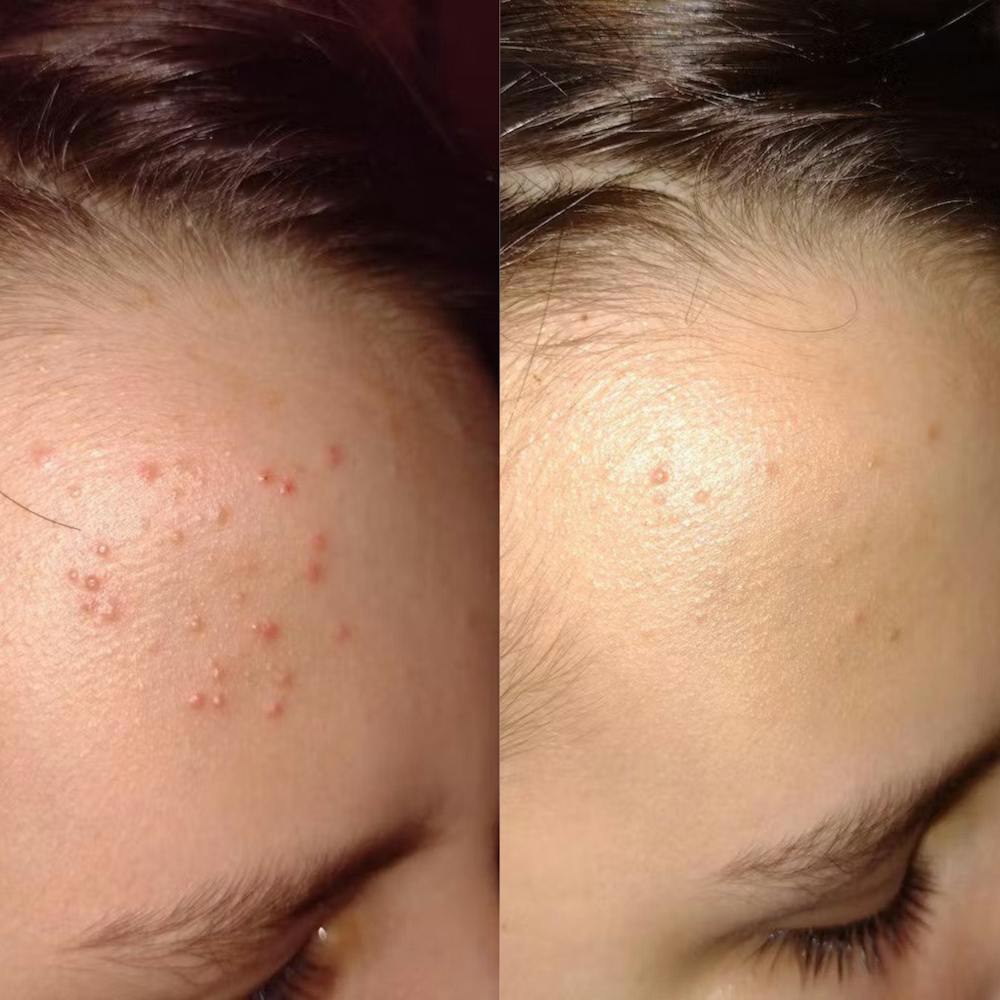
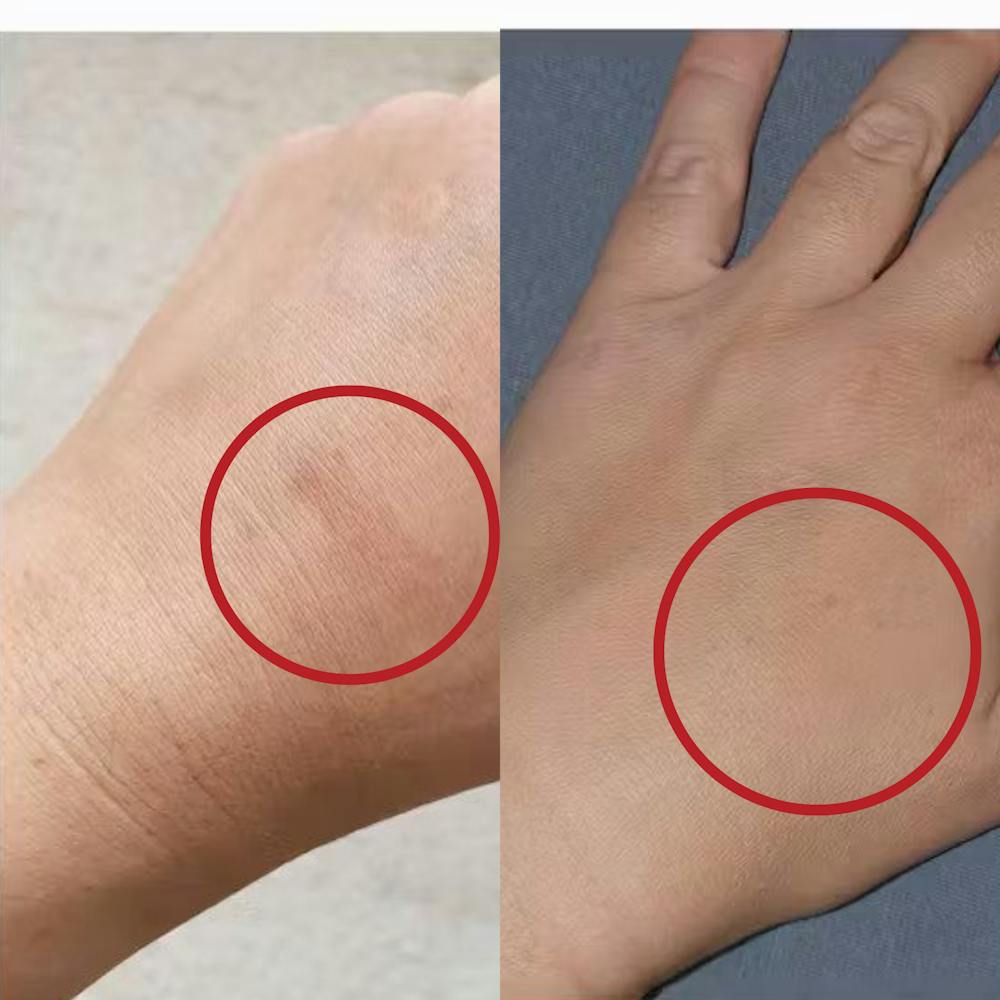
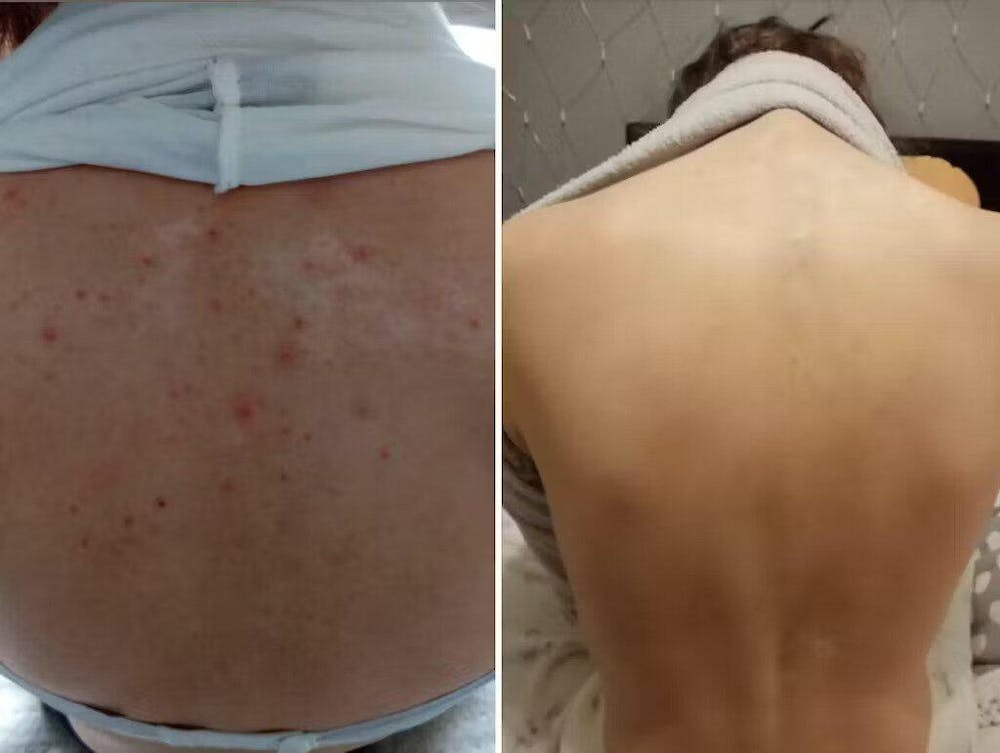
Introducing the Eczema RoutINA™: A Path to Lasting Relief
-
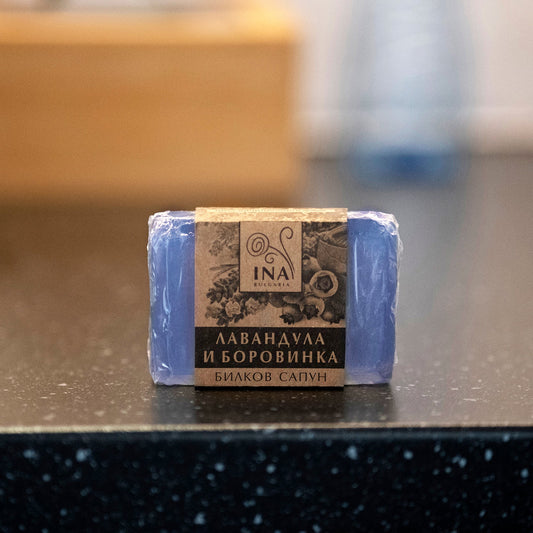
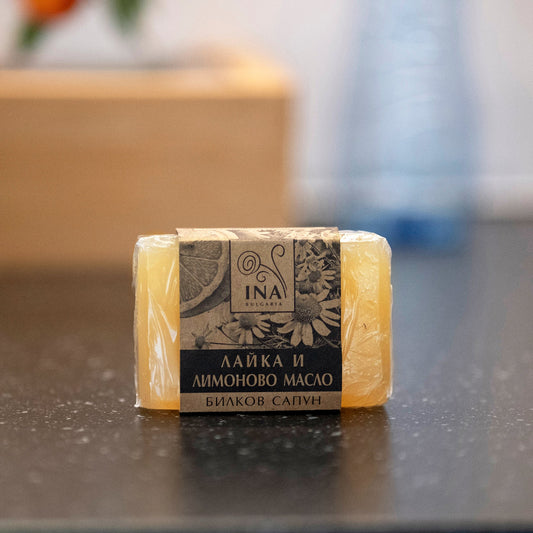
Natural Herbal Soap with Chamomile and Lemon Oil (110g):This gentle soap cleanses without stripping the skin's natural oils, leaving it feeling calm and comfortable.
-
Organic Chamomile Water - Hydrolina for Eczema and Irritated Skin (150ml): This soothing hydrolat mist delivers a refreshing dose of organic chamomile, known for its anti-inflammatory and calming properties.
-
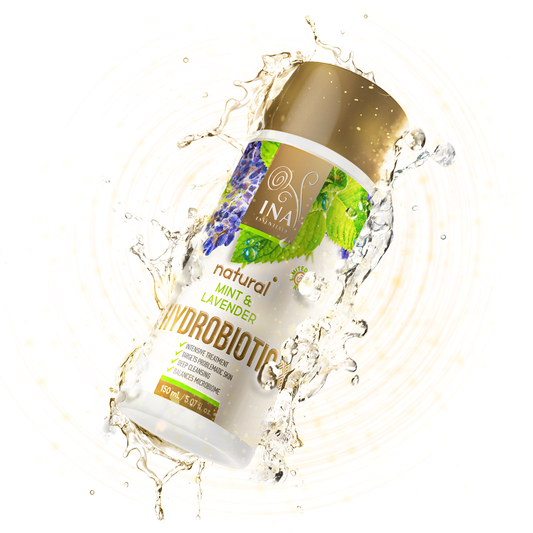
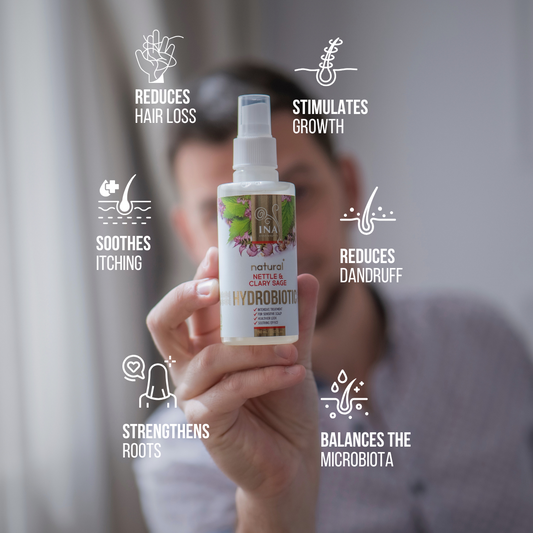
Hydrobiotic—Chamomile, Melissa & Aloe Vera (150ml): This innovative blend of chamomile, lemon balm, and aloe vera postbiotic provides deep hydration and promotes skin healing.
The power of Chamomile